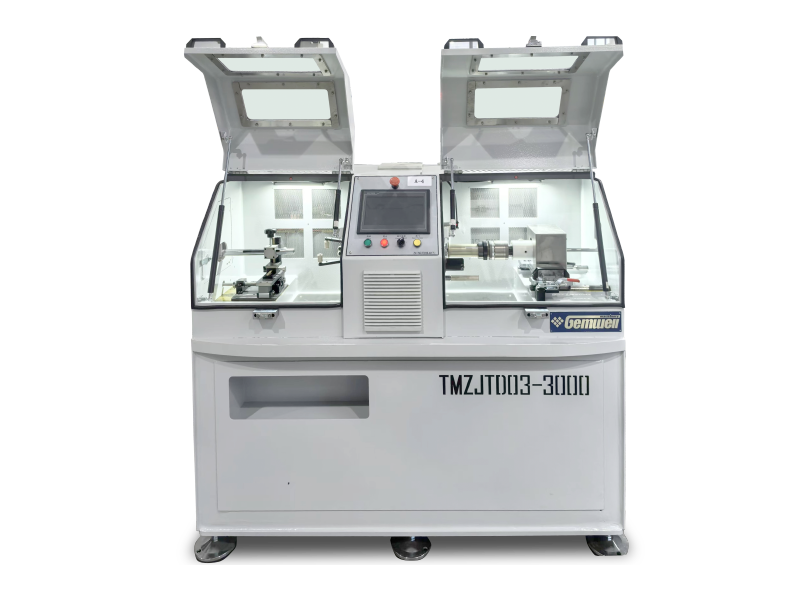
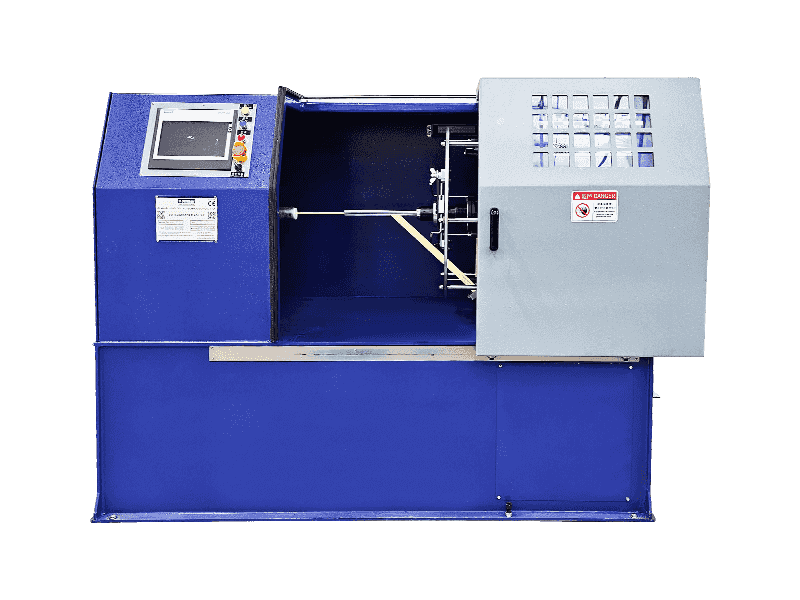
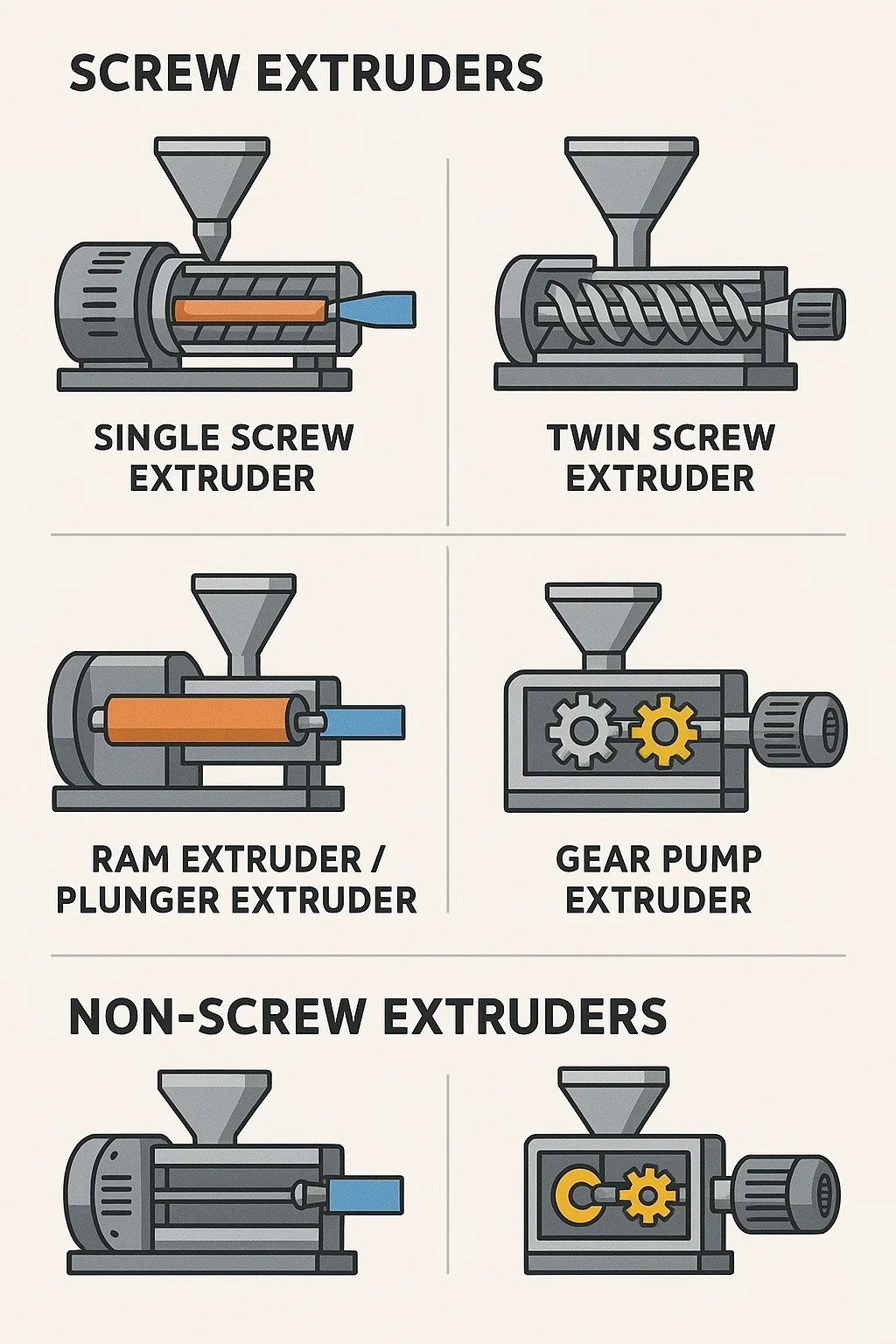
In fields such as plastics, metals, and food processing, extrusion machines can be primarily classified into the following categories based on their working principles and structure:
Content
1. Screw Extruders
These are the most common and widely used type of extrusion machine. They rely on one or more rotating screws to propel, heat, mix, and pressurize the material forward, then extrude it through a die for shaping.
• Single Screw Extruders:
Features: The machine has only one screw. The structure is relatively simple, the cost is lower, and maintenance is easy.
Applications: Primarily used in scenarios where high material mixing is not required and stable, continuous output is needed, such as the production of pipes, sheets, and films.
• Twin Screw Extruders:
Features: The machine has two intermeshing or non-intermeshing screws. They typically provide stronger shear force and better mixing effects.
Types:
-- Co-rotating Twin Screw: The two screws rotate in the same direction. They offer excellent mixing and dispersion performance and are the main type of extrusion machine for polymer modification, compounding, and granulation.
-- Counter-rotating Twin Screw: The two screws rotate in opposite directions. Often used in applications requiring high material conveying pressure, such as PVC pipe production.
2. Ram Extruders / Plunger Extruders
These extrusion machines do not use screws, but instead use a ram or piston to push the material from the barrel towards the die.
Features: They operate intermittently, rather than continuously. This method allows for the application of extremely high pressure to the material.
Applications: Particularly suitable for processing materials that are prone to degradation or are shear-sensitive during screw extrusion, such as certain ultra-high molecular weight polymers, ceramic slurries, or certain fluoroplastics (e.g., PTFE).
3. Non-Screw Extruders
These refer to extrusion machines that do not rely on traditional screw structures to achieve the extrusion purpose, and are mainly used in specific processing applications.
• Gear Pump Extruders:
Features: They use a set of precisely meshing gears to convey and pressurize the molten material, rather than relying on a screw.
Applications: This method provides very stable and precise extrusion volume and pressure, and is often used to improve the metering accuracy of traditional screw extrusion systems, such as in the production of precision films and fibers.
• Friction Extruders:
Features: This type of machine softens and mixes materials by generating significant frictional heat through the relative motion of mechanical components, and then extrudes them.
Applications: Commonly found in the metal processing field, it can be used for continuous extrusion molding of certain difficult-to-process alloys.
 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products