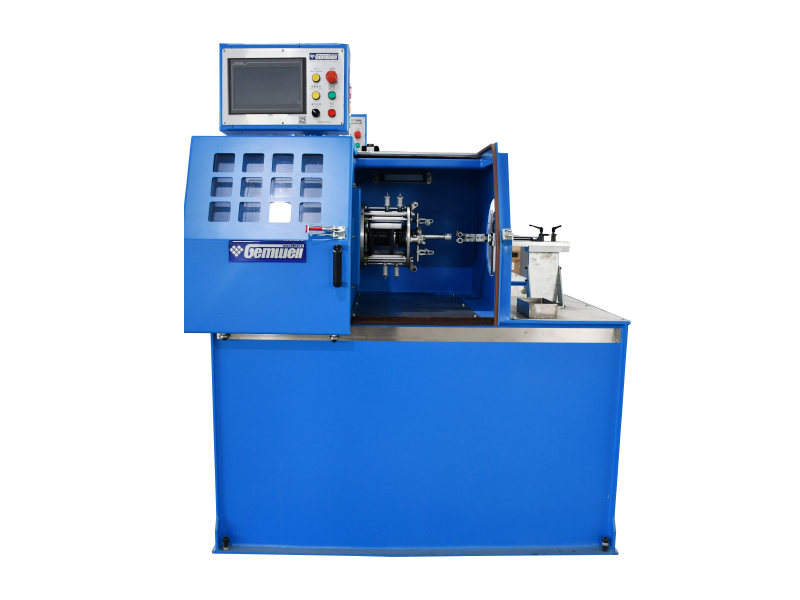
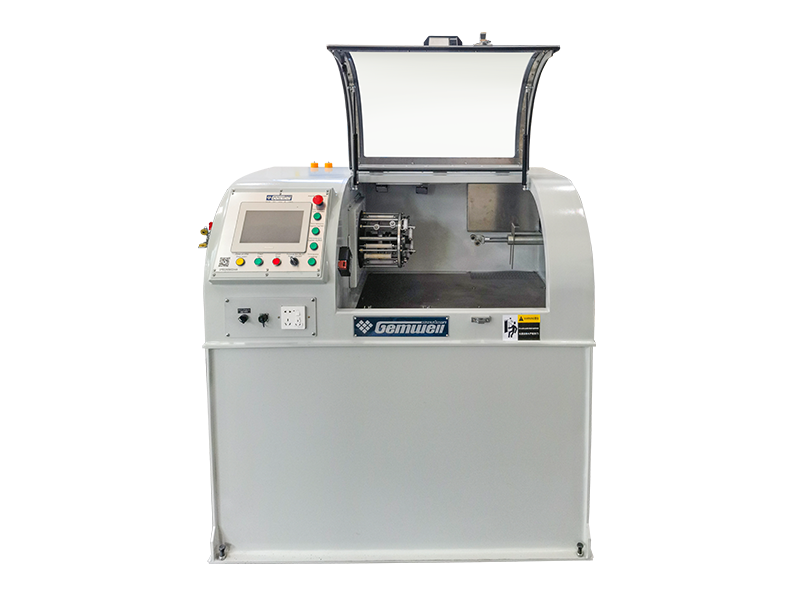
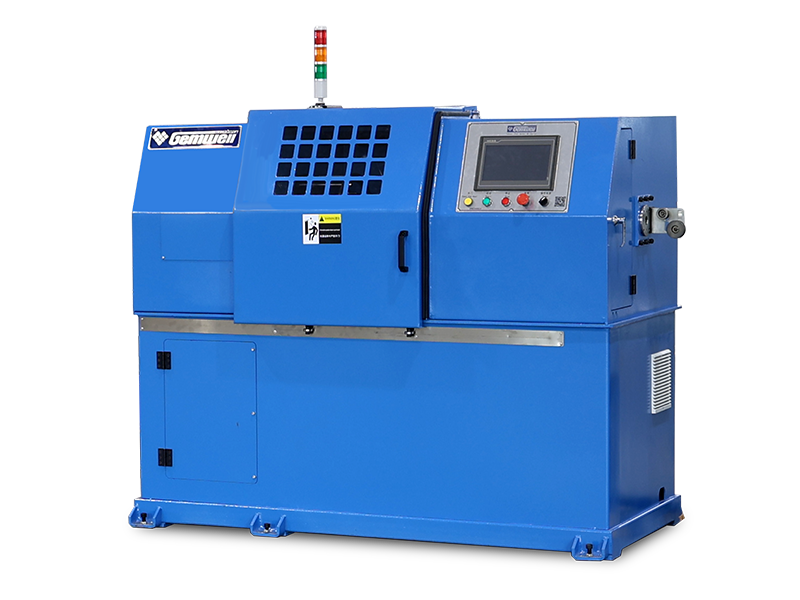
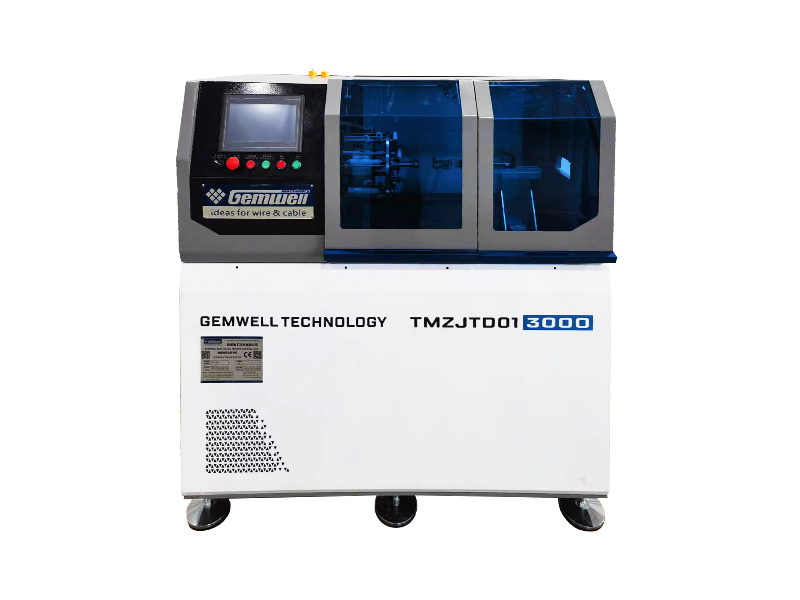
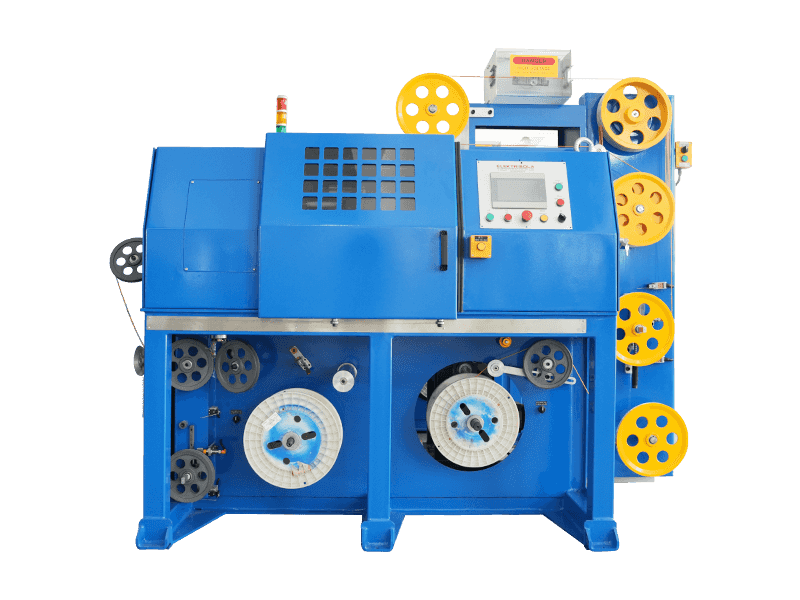
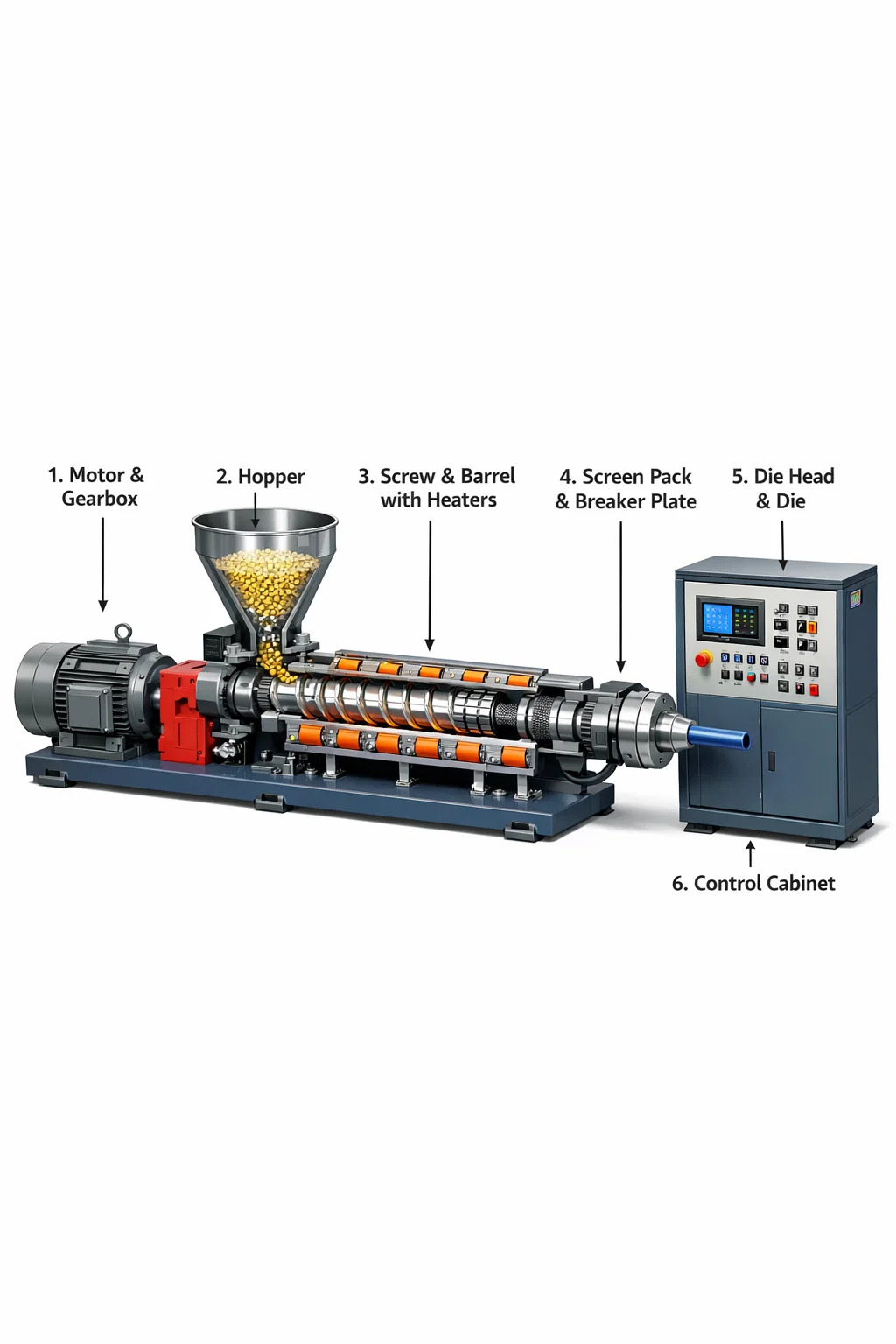
Although an extruder machine looks like a bulky, heavy metal cabinet, its internal structure is very sophisticated. We can imagine it as a "superheated mixing pump," mainly composed of the following core parts:
Content
1. Power Heart: Motor & Gearbox
This is the source of the machine's "strength."
Motor: Provides rotational power, like the motor of an electric fan.
Gearbox: The motor rotates very fast, but the extruder needs "slow and steady" power. The gearbox reduces the rotational speed while amplifying the force to drive the heavy screw.
2. Feeding Area: Hopper
This is the machine's "mouth."
This is a funnel-shaped container installed on top of the machine. You pour plastic pellets, powder, or metal pieces into it, and they will fall into the machine through the funnel.
3. Processing Workshop: Screw & Barrel
This is the most crucial part of the extruder.
Barrel: A thick, long metal tube that encloses the screw and can withstand extremely high pressure.
Screw: A huge spiral-shaped part lying inside the barrel. When it rotates, it pushes the raw materials forward like a screw.
Heaters: Rings of heating elements attached to the outside of the barrel. They heat the barrel, allowing the raw materials inside to gradually melt into a "slurry" during the pushing process.
4. Protective Barrier: Screen Pack & Breaker Plate
After the raw materials melt into a "slurry," they must pass through a barrier before flowing out.
Breaker Plate: A steel plate with many small holes that transforms turbulent liquid flow into a straight flow.
Screen Pack: Located tightly against the breaker plate, it filters out any unmelted pieces or dust from the raw materials, ensuring a clean output.
5. Mold: Die Head & Die
This is the "mold" that determines the shape of the finished product.
The filtered raw material is pushed to the very front of the machine.
The die head is the connecting part, and the die is an outlet with a specific shape. The raw material is forcefully extruded from this outlet, instantly transforming into the shape of tubes, sheets, or profiles.
6. Control Center: Electrical Control Cabinet (Control System)
This is the "brain" of the machine.
It has many knobs, switches, or touchscreens used to adjust which section of the barrel should be heated and how fast the screw should rotate. The operator gives commands here to ensure the entire extruder operates correctly.

 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products