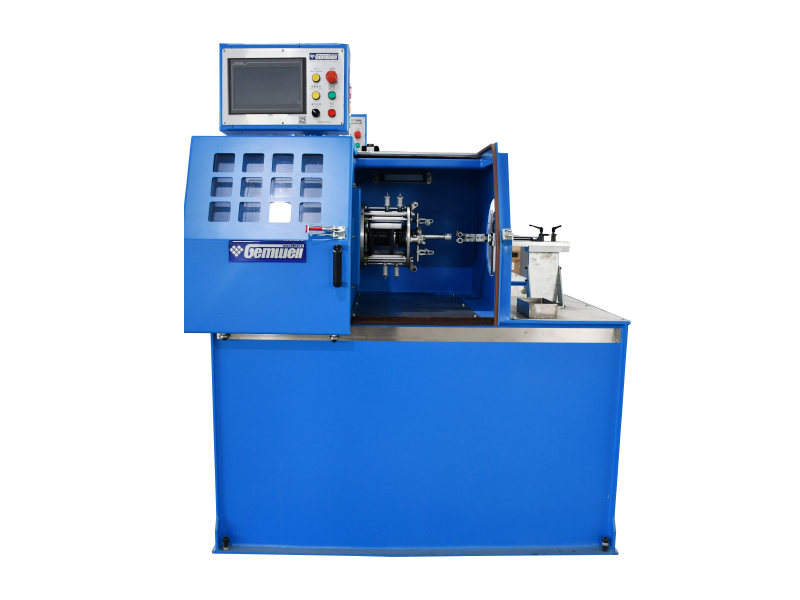
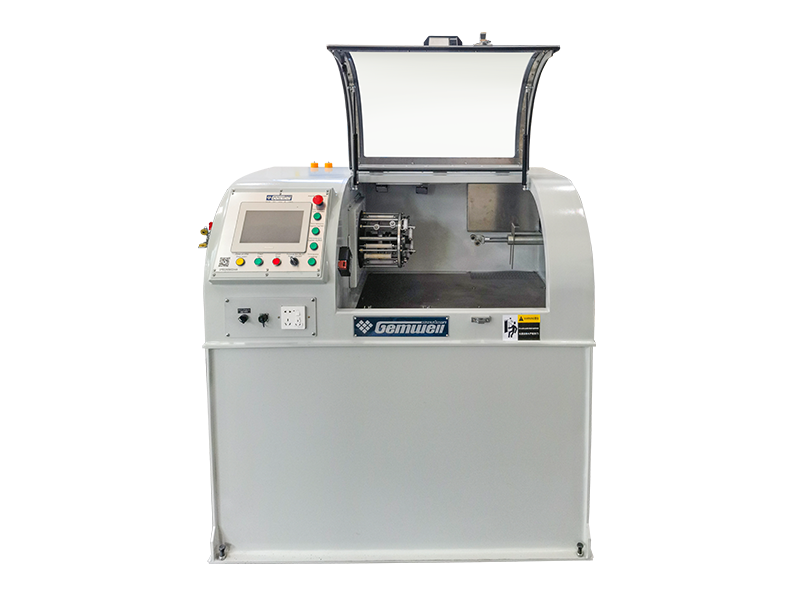
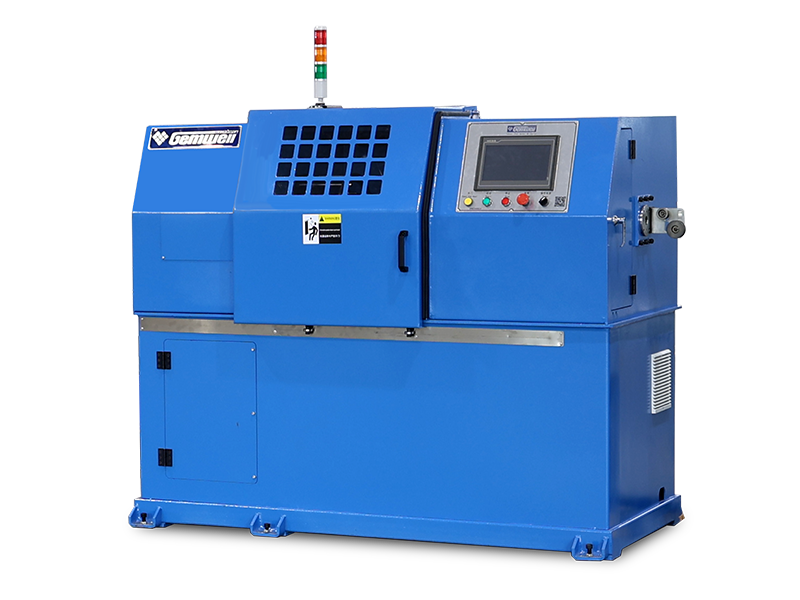
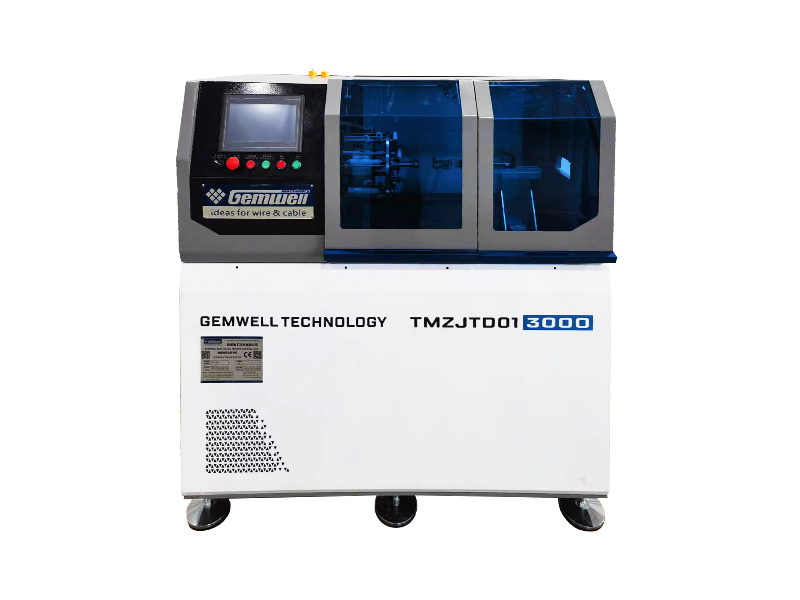
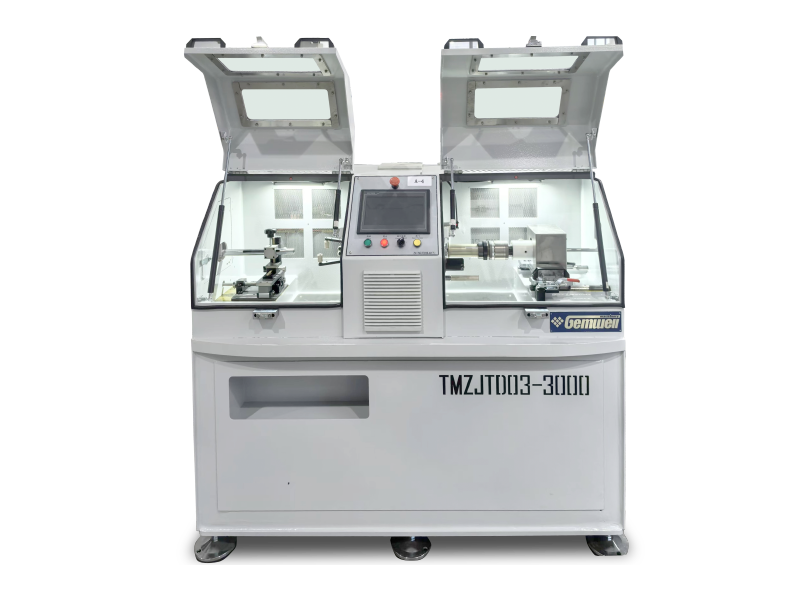
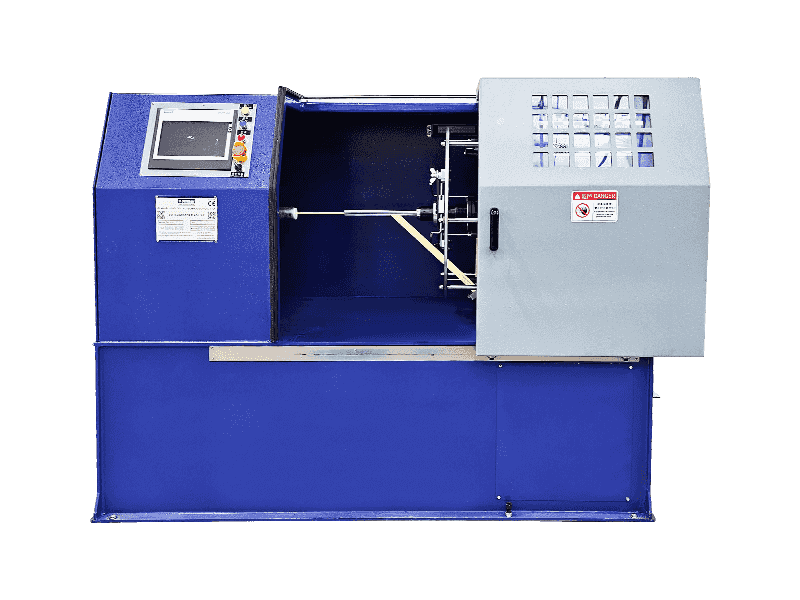
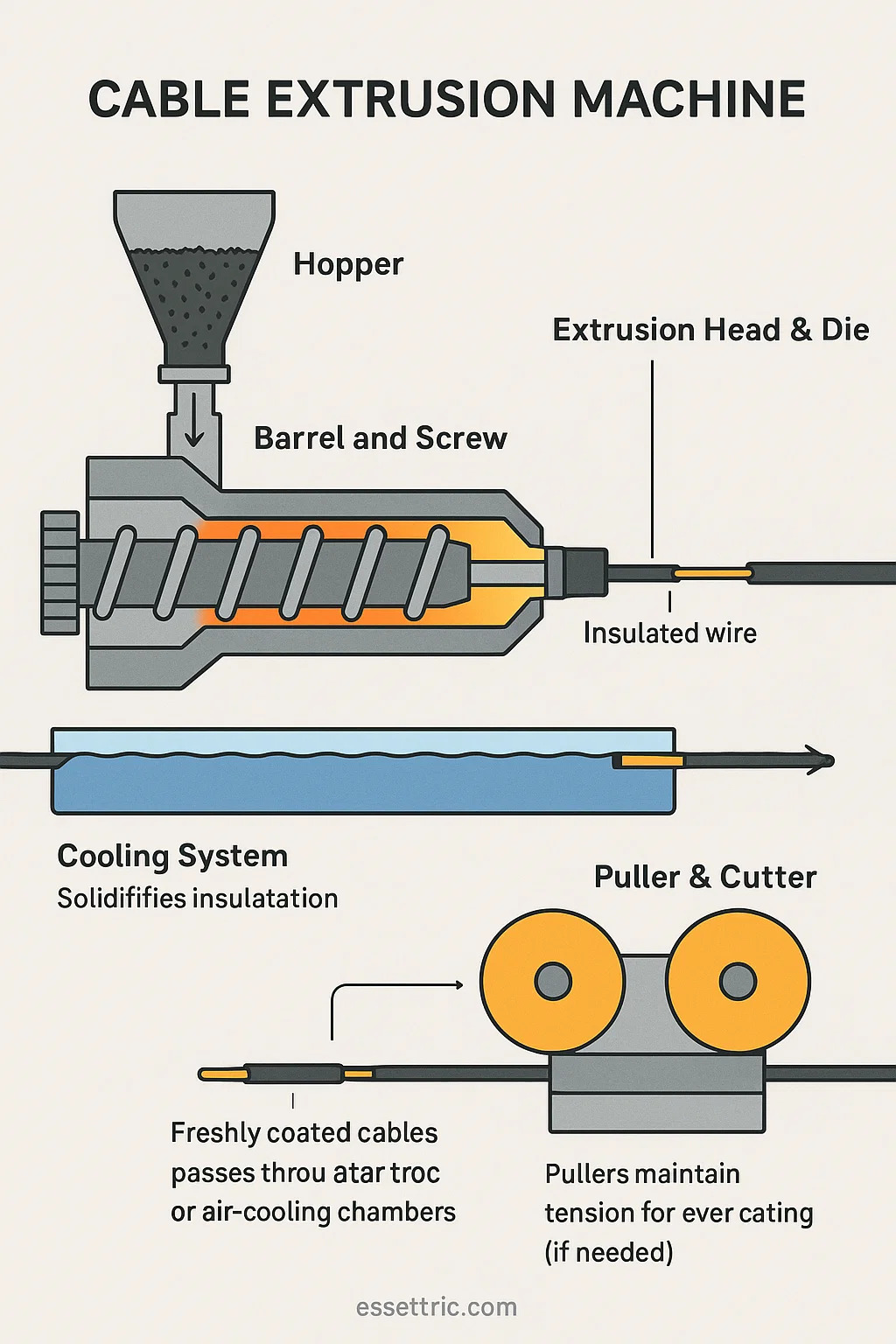
A cable extrusion machine is central to wire and cable manufacturing. It applies protective or functional layers—like insulation or outer sheathing—onto conductors. Here’s how it works in practice:
●Core Function
Material Coating — Melts raw plastic or rubber compounds (e.g., PVC, XLPE) into a fluid state. — Uniformly coats wires or cable cores as they pass through the machine.
●Key Components
▸Hopper
— Raw material (pellets/powder) is fed here. Gravity moves it into the barrel.
▸Barrel and Screw
— The barrel heats material while a rotating screw mixes and pushes it forward.
— Gradually melts the material into a viscous fluid.
▸Extrusion Head & Die
— Molten material is forced through the head.
— A precisely shaped die molds it around the moving conductor.
▸Cooling System
— Freshly coated cables pass through water troughs or air-cooling chambers.
— Solidifies the insulation/sheathing quickly to retain shape.
▸Puller & Cutter
— Pullers maintain tension for even coating.
— Cutters trim cables to preset lengths (if needed).
| Aspect | Description |
| Primary Function | Applies insulation, sheathing, or functional layers onto wires/cable cores. |
| Core Components | - Hopper: Feeds raw material (e.g., PVC, XLPE pellets). - Barrel & Screw: Heats, melts, and mixes material. - Die: Shapes molten material around the conductor. - Cooling System: Solidifies coating (water/air). - Puller: Maintains tension during extrusion. |
| Process Flow | 1. Conductor fed into machine. 2. Material melted in barrel. 3. Die coats conductor. 4. Cooling sets the layer. 5. Cable wound onto reels. |
| Key Outputs | - Insulated wires. - Jacketed multi-core cables. - Shielding/semi-conductive layers. |
| Specialized Features | - Dual extrusion: Applies two layers simultaneously. - Cross-linking: Enhances material strength (e.g., XLPE). - Color striping: Adds identification lines. |
| Material Flexibility | Works with thermoplastics (PVC, PE), rubber, and cross-linked polymers. |
| Customization | Adjusts for coating thickness, diameter, and material via interchangeable dies. |
| Quality Control | Sensors monitor thickness uniformity; auto-adjusts temperature/speed. |
 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products