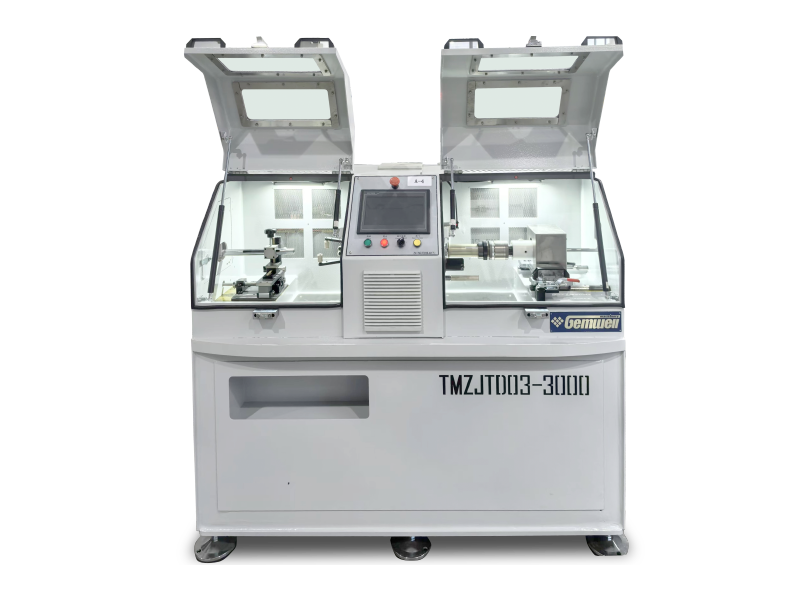
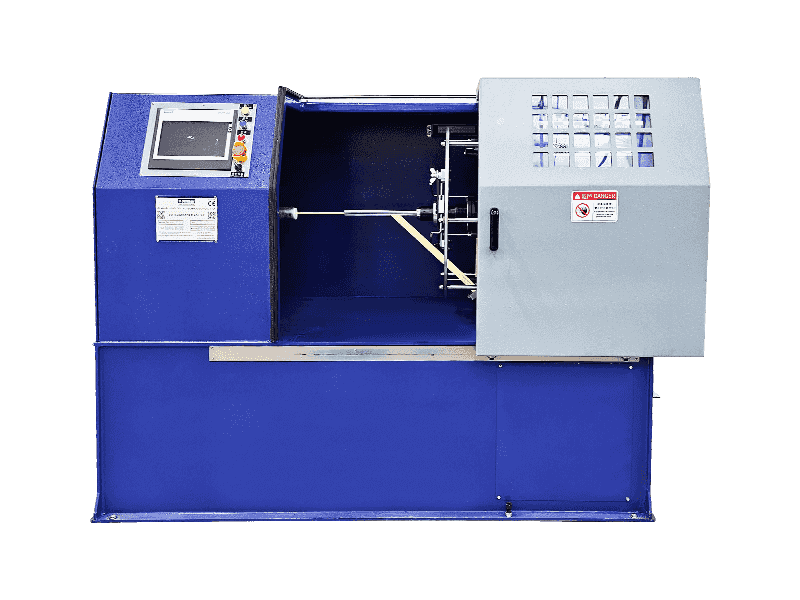
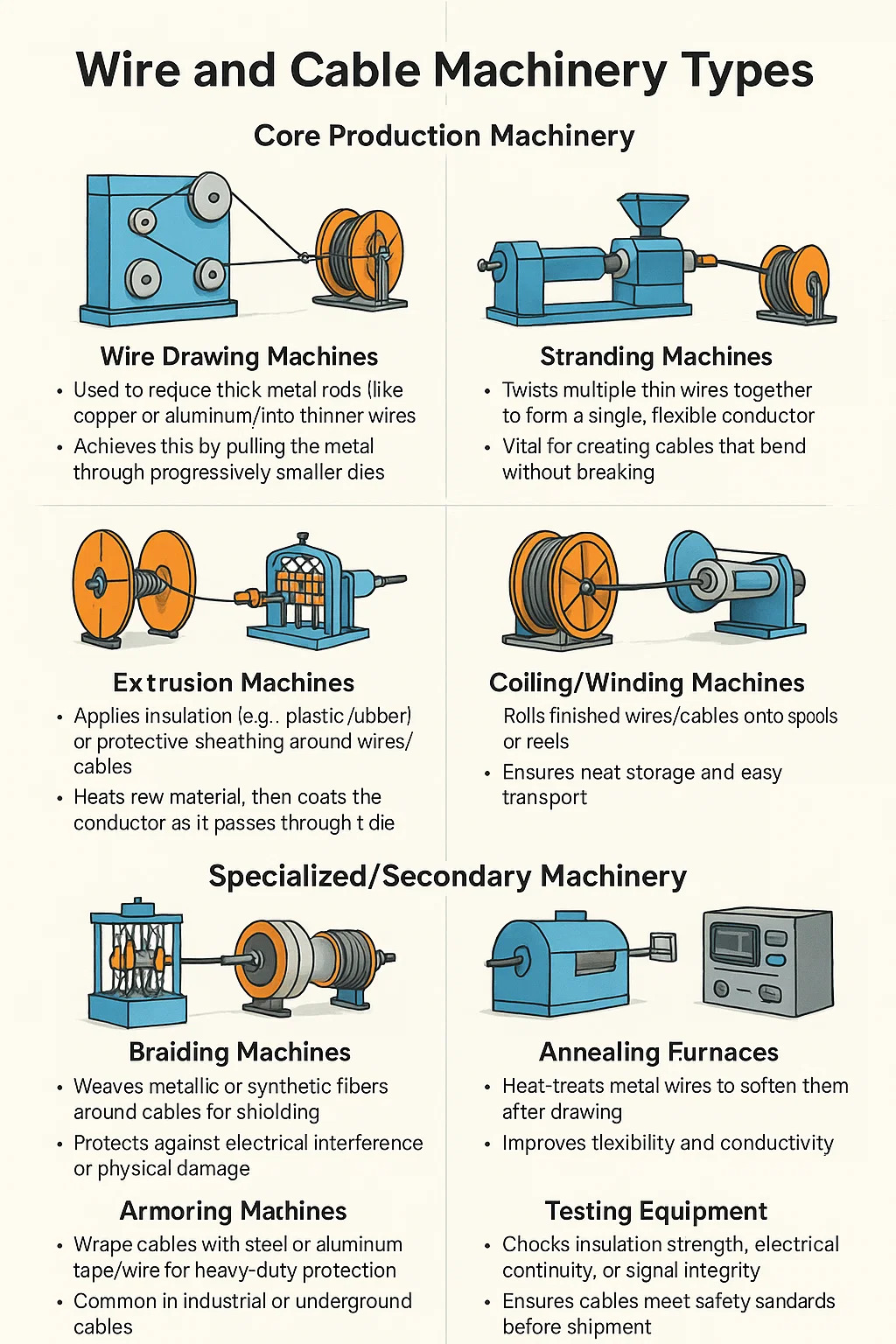
Based on common industry knowledge, here's a breakdown of wire and cable machinery types:
●Core Production Machinery
Wire Drawing Machines
— Used to reduce thick metal rods (like copper or aluminum) into thinner wires.
— Achieves this by pulling the metal through progressively smaller dies.
●Stranding Machines
— Twists multiple thin wires together to form a single, flexible conductor.
— Vital for creating cables that bend without breaking.
●Extrusion Machines
— Applies insulation (e.g., plastic, rubber) or protective sheathing around wires/cables.
— Heats raw material, then coats the conductor as it passes through a die.
●Coiling/Winding Machines
— Rolls finished wires/cables onto spools or reels.
— Ensures neat storage and easy transport.
●Specialized/Secondary Machinery
Braiding Machines
— Weaves metallic or synthetic fibers around cables for shielding.
— Protects against electrical interference or physical damage.
●Armoring Machines
— Wraps cables with steel or aluminum tape/wire for heavy-duty protection.
— Common in industrial or underground cables.
●Annealing Furnaces
— Heat-treats metal wires to soften them after drawing.
— Improves flexibility and conductivity.
●Testing Equipment
— Checks insulation strength, electrical continuity, or signal integrity.
— Ensures cables meet safety standards before shipment.
●Support Machinery
Wire Cleaning/Treatment Lines
— Removes oxides, oils, or residues from metal surfaces before insulation.
— Ensures strong adhesion of coatings.
●Marking Machines
— Prints text (e.g., specs, brand names) directly onto cable sheaths.
— Uses ink jets or embossing.
 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products