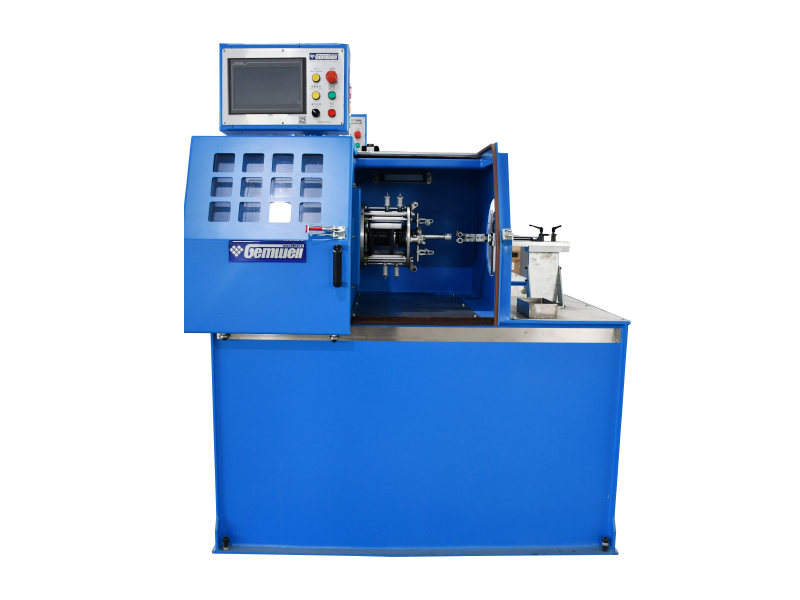
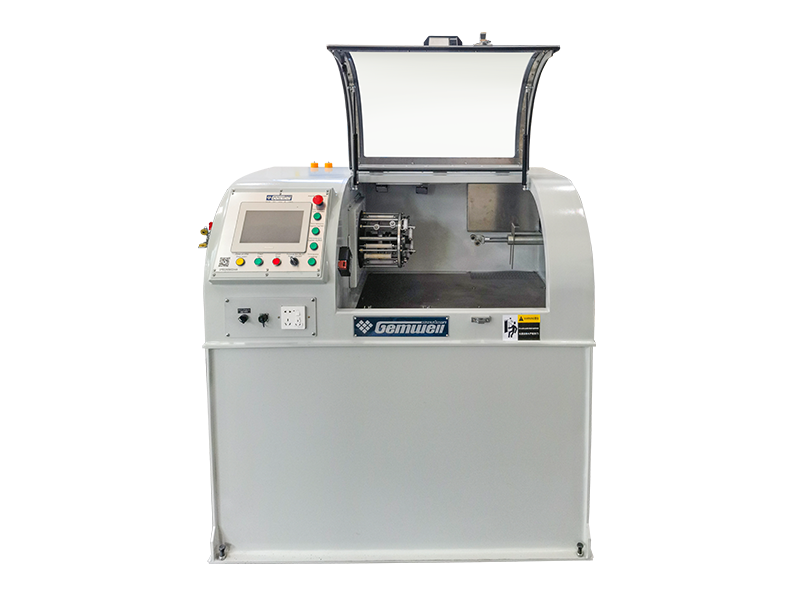
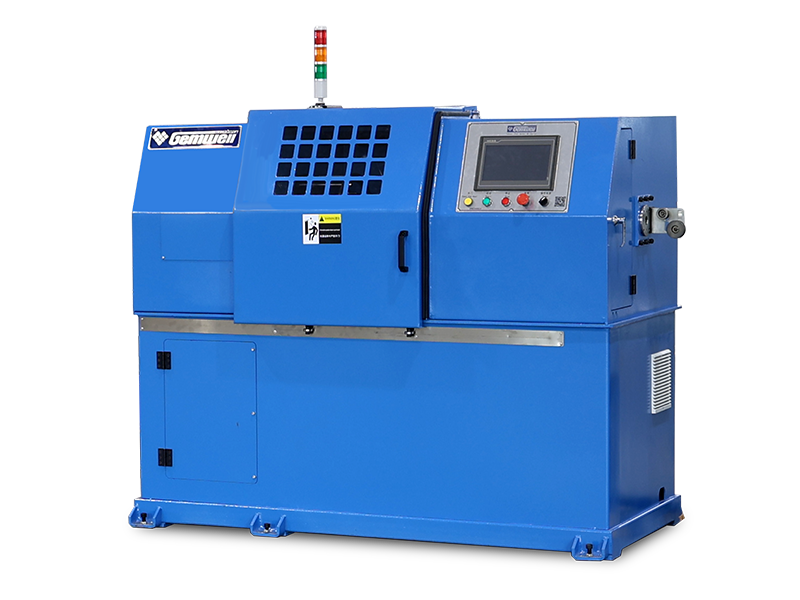
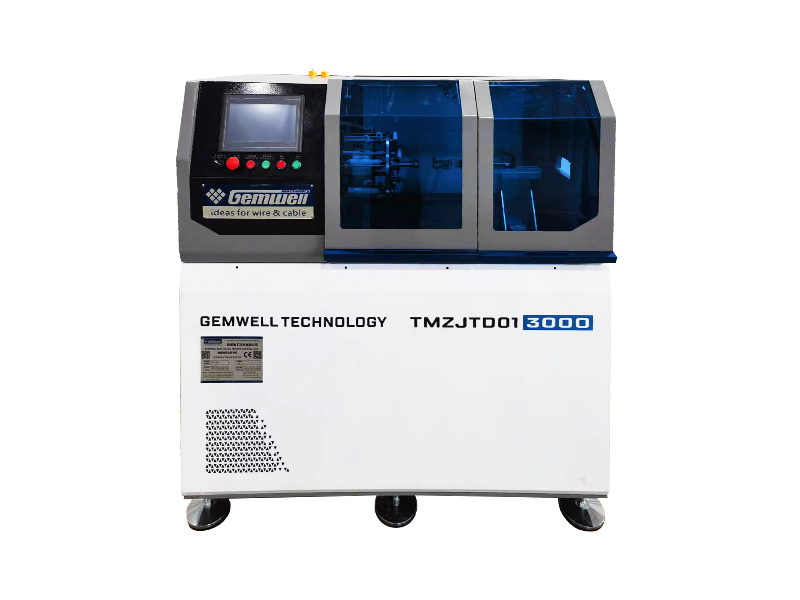
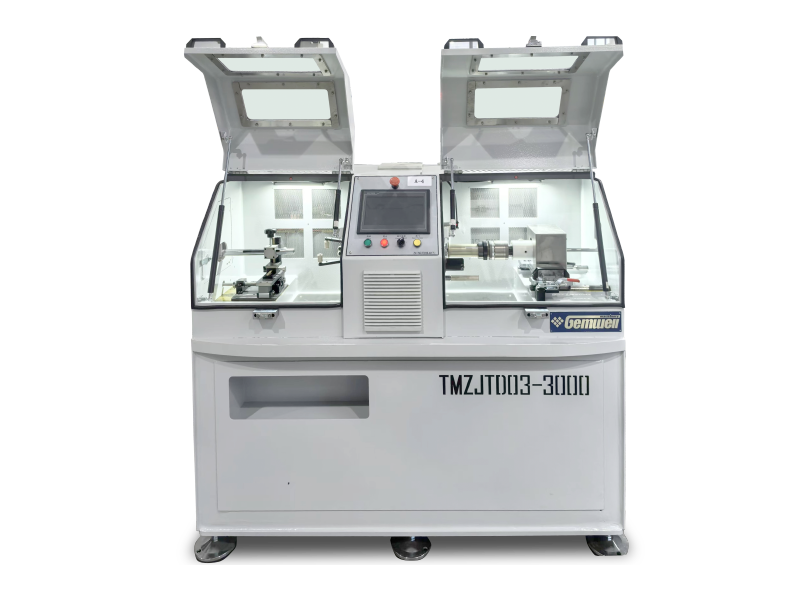
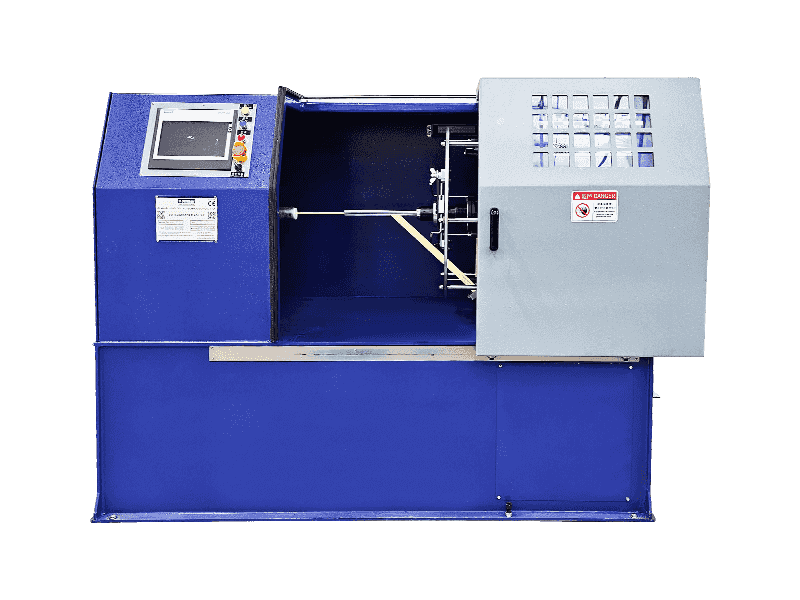
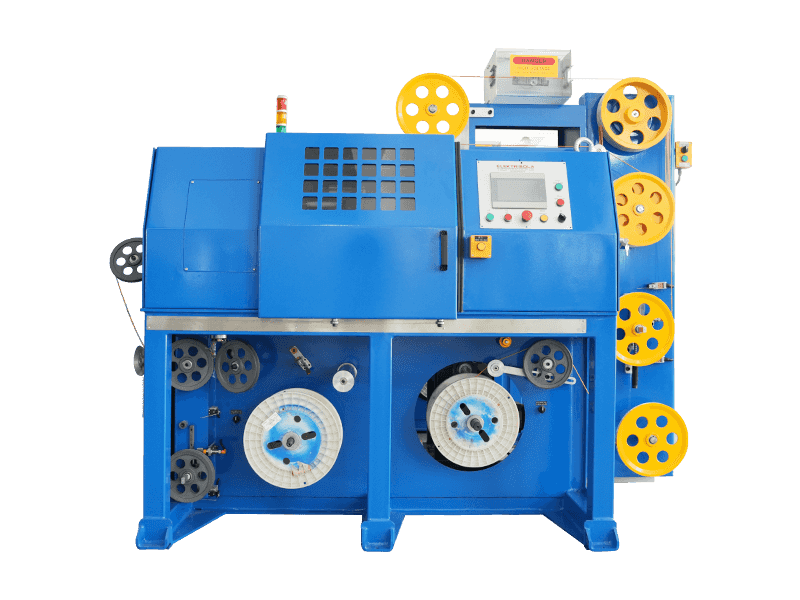
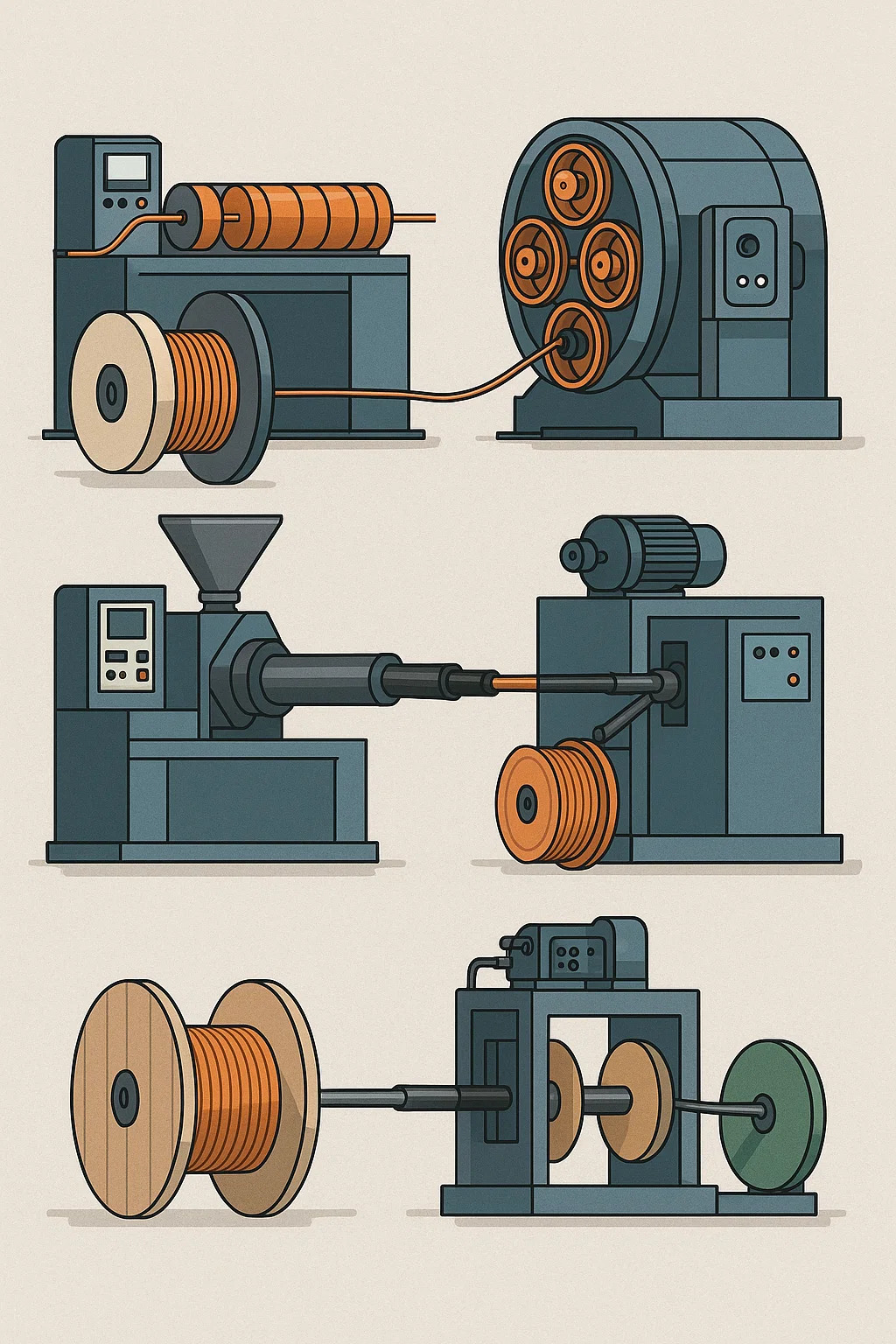
Wire and cable machinery refers to the equipment used in the manufacturing of electrical wires and cables. Here's a breakdown of its key aspects:
Purpose – Designed to produce various types of wires and cables, including power cables, communication cables, and specialty cables.
Main Processes – Handles multiple stages of production, such as wire drawing, stranding, insulation, shielding, and sheathing.
Types of Machines
| Machine Type | Function |
| Wire Drawing Machine | Reduces the diameter of metal rods (copper/aluminum) to form thin, uniform wires. |
| Stranding Machine | Twists multiple wires together to create flexible stranded conductors. |
| Extrusion Machine | Applies insulation (PVC, XLPE, rubber) or sheathing over conductors. |
| Coiling/Winding Machine | Winds finished cables onto spools or reels for storage and transportation. |
| Braiding Machine | Adds metallic or textile braided shielding for protection against interference. |
| Annealing Machine | Heat-treats wires to improve flexibility and conductivity. |
| Testing Equipment | Checks electrical properties, insulation integrity, and dimensional accuracy. |
Automation Level – Modern machinery often includes automated controls for precision and efficiency, reducing manual intervention.
Material Compatibility – Works with metals like copper and aluminum, as well as insulating materials such as PVC, XLPE, and rubber.
Applications – Serves industries like construction, telecommunications, automotive, and energy distribution.
Customization – Some machines can be adjusted to produce different wire gauges, insulation thicknesses, and cable configurations.
Safety & Compliance – Designed to meet industry standards for electrical safety and performance.
 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products