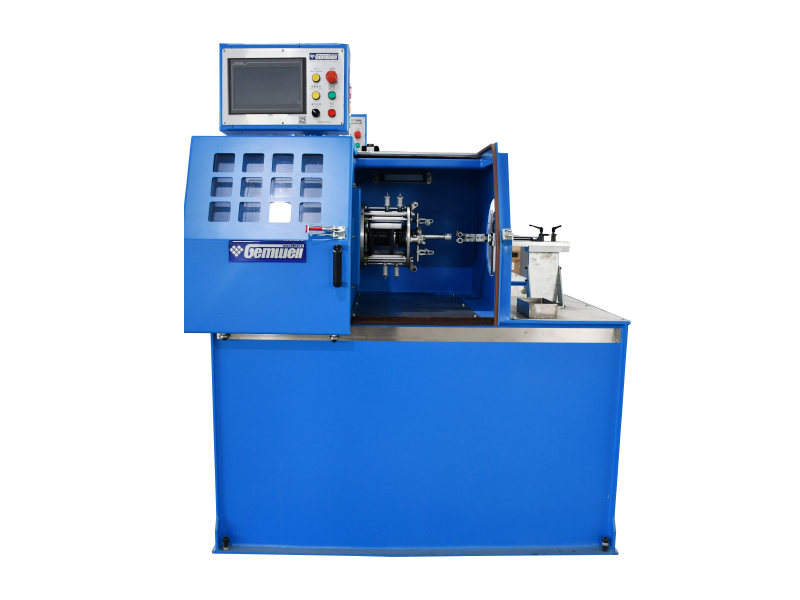
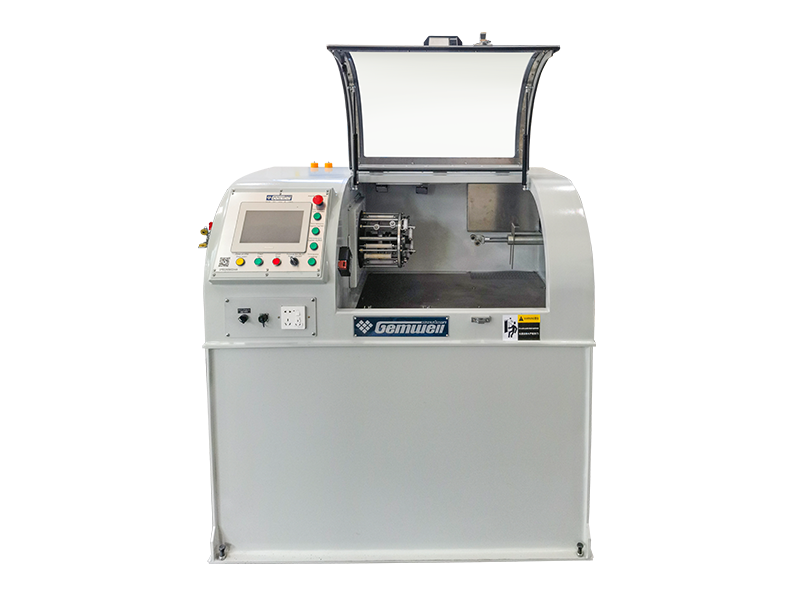
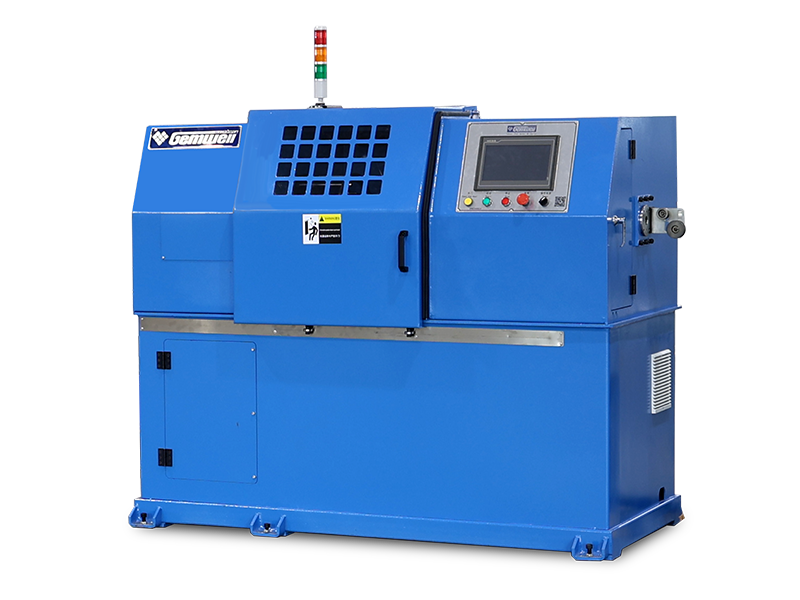
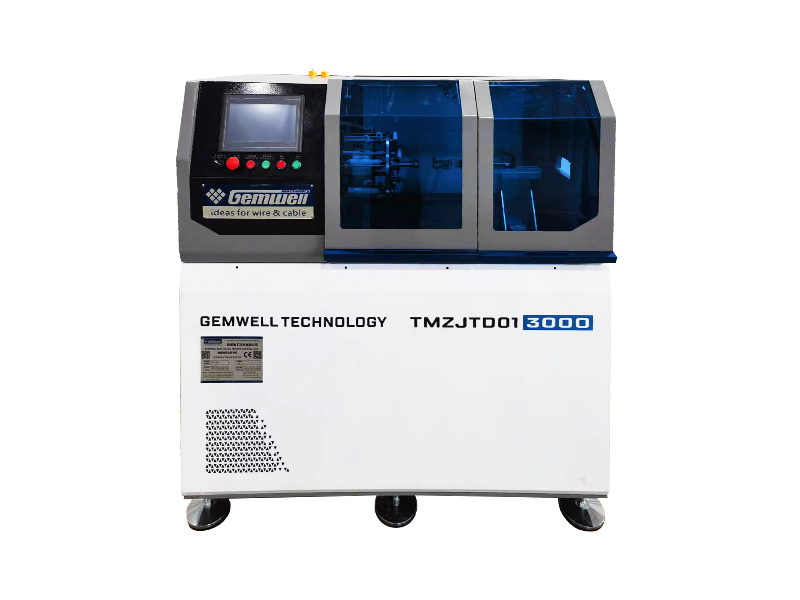
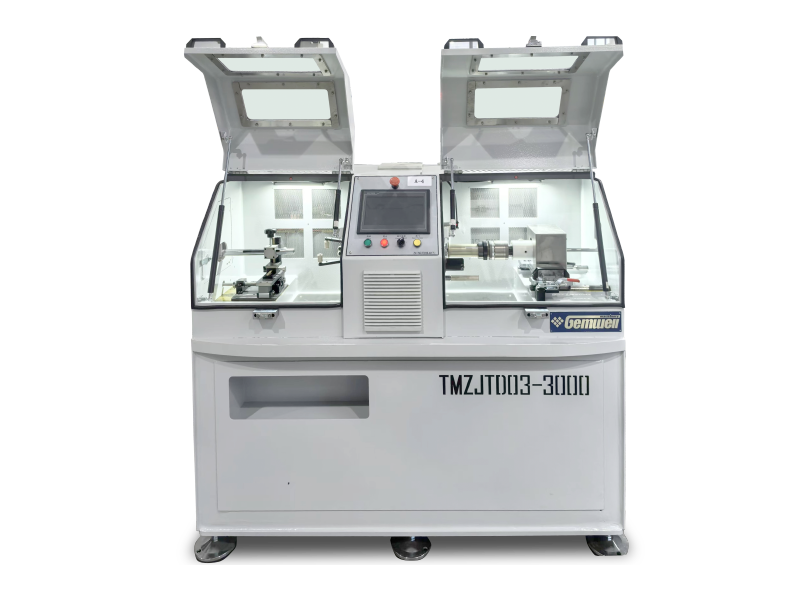
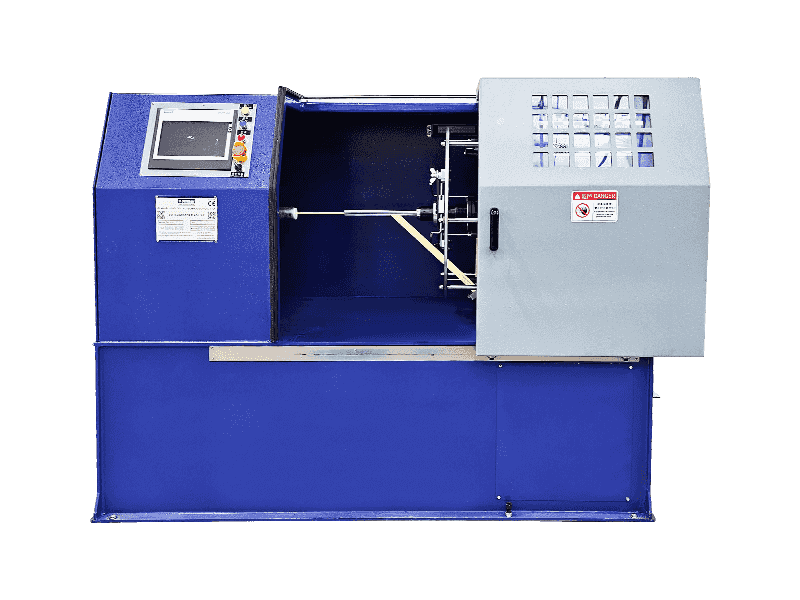
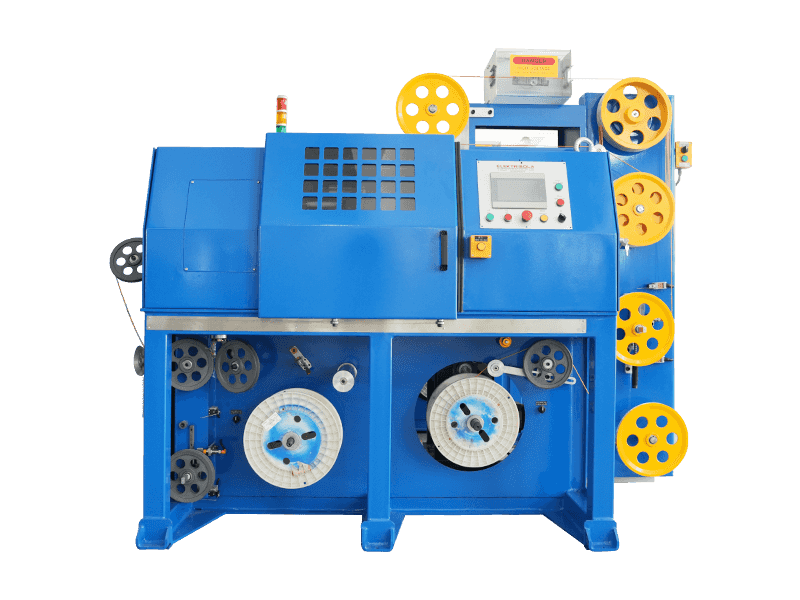
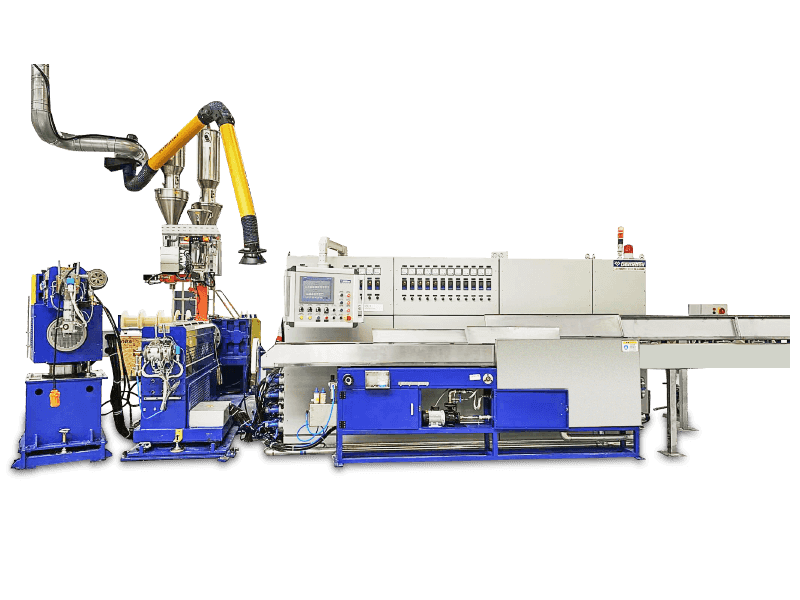
The Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine is a critical piece of equipment in the manufacturing of electrical and communication cables. It is used to apply a protective sheath or coating onto the core of a cable, ensuring durability, insulation, and protection from environmental factors.
1. What is a Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine?
1.1 Definition and Function
- A Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine is a machine that uses the extrusion process to apply a thermoplastic or thermosetting material (such as PVC, PE, PP, or TPE) onto a cable core. This process forms a protective sheath around the cable.
- The machine typically includes components such as:
- Extruder: The core component that melts and extrudes the material.
- Die: The part that shapes the extruded material into the desired shape.
- Cooling System: To cool the extruded material quickly.
- Pay-off and Take-up Systems: To handle the incoming and outgoing cable.
1.2 Key Functions
- Protection: The sheath protects the cable from moisture, UV radiation, and mechanical damage.
- Insulation: Provides electrical insulation.
- Aesthetics: Improves the appearance of the cable.
2. Key Components of a Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine
| Component |
Description |
Function |
| Extruder |
The core component that melts and extrudes the sheath material (e.g., PVC, PE) onto the wire core. |
Melts and shapes the material into the desired form. |
| Pay-off and Take-up Systems |
Systems that unwind the wire from the supply reel and reel in the finished product. |
Ensures consistent tension and proper handling of the wire. |
| Cooling System |
Used to cool the extruded sheath to maintain quality and prevent deformation. |
Essential for maintaining the integrity of the extruded product. |
| Control Systems |
Includes PLC and automation systems for precise operation and monitoring. |
Ensures accurate control of the extrusion process. |
| Auxiliary Equipment |
Includes tension control systems, cooling troughs, and other support systems. |
Supports the overall operation and quality of the extrusion process. |
| Screws and Barrel |
The core components of the extruder, responsible for melting and conveying the material. |
Works with the barrel to process and shape the material. |
| Die |
The component that shapes the extruded material into the final product. |
Determines the final shape and structure of the extruded product. |
| Hopper and Drive Motor |
The hopper feeds the raw material into the extruder, and the drive motor powers the extrusion process. |
Ensures the continuous flow of material and energy input. |
3. Key Technical Specifications
3.1 Extrusion Process
- Material Compatibility: The machine can handle a variety of materials, including PVC, PE, PP, TPE, and others.
- Extrusion Speed: The rate at which the material is extruded, typically measured in meters per minute (m/min).
- Output Capacity: The amount of material that can be processed per hour.
3.2 Machine Components
- Extruder: The heart of the machine, responsible for melting and extruding the material.
- Die: The part that shapes the extruded material.
- Cooling System: Essential for rapid cooling of the extruded material.
- Control Systems: PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) for automation and control.
3.3 Power and Drive Systems
- Motors and Servo Systems: Used for precise control of the extrusion process.
- Cooling Systems: Water or air-cooled systems to maintain optimal temperature.
| Parameter |
Details |
| Extrusion Material |
PVC, PE, PP, PVC, Low-smoke zero-halogen, Conductive materials |
| Extrusion Speed |
Up to 60 m/min (varies by machine) |
| Output Capacity |
600 kg/h (varies by material and machine) |
| Power Requirements |
3-phase, 480V, 60Hz, 90kW motor |
| Cooling Method |
Water cooling, air cooling |
| Control System |
PLC, Siemens, Yaskawa, Omron |
| Tension Control |
Pneumatic, magnetic, electronic |
4. Key Features and Capabilities
| Feature/Capability |
Description |
| Material Compatibility |
The machine can process a wide range of materials such as PVC, PE, PP, and others, depending on the application . |
| High Productivity |
Machines are designed for high productivity, with output capacities ranging from 100 kg/h to 250 kg/h or more . |
| Precision Control |
Advanced control systems (e.g., PLC, Siemens) ensure precise operation and monitoring of the extrusion process . |
| Quality Control |
Features such as temperature control, concentricity, and cooling systems ensure high-quality extrusion . |
| Automation and Flexibility |
Many machines offer automated operations, including automatic reel handling, tension control, and programmable settings . |
| Durability and Reliability |
Use of high-quality components (e.g., Siemens motors, NSK bearings) and robust design ensures long-term reliability . |
| Versatility |
Capable of handling various cable types, including power cables, building wires, and optical fiber cables . |
| After-Sales Service |
Many manufacturers offer installation, training, and after-sales support . |
5. Common Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge |
Solution |
| Burnt or Discolored Sheath |
Adjust heating temperature to avoid overheating; monitor extrusion temperature closely |
| Uneven Product Diameter |
Adjust extrusion speed, check die alignment, and ensure proper concentricity |
| Material Clogging or Blockage |
Clean the extruder, filter screen, and die; ensure proper material flow |
| Inconsistent Material Flow |
Optimize temperature control, adjust screw design, and ensure proper material feeding |
| Poor Surface Finish |
Adjust extrusion temperature and ensure proper cooling |
| Excessive Wear and Tear |
Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and timely replacement of worn parts |
| Inconsistent Product Quality |
Implement quality control checks, monitor extrusion parameters, and adjust settings as needed |
6. Applications and Industries
6.1 Industries Served
- Power Industry: Used for power cables, transformers, and electrical installations.
- Communication Industry: Used for optical fiber cables, coaxial cables, and data cables.
- Building and Construction: Used for building wires, cables in buildings, and infrastructure.
- Automotive Industry: Used for automotive cables and wiring harnesses.
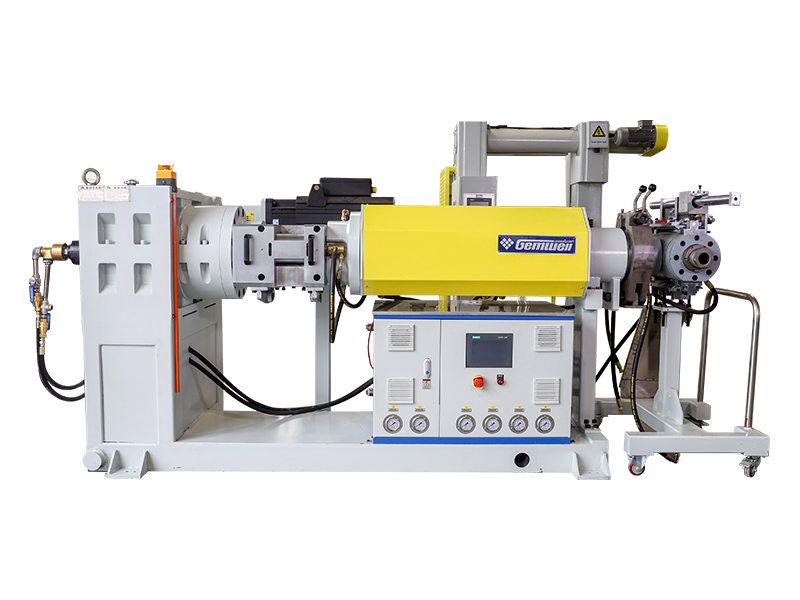

6.2 Cable Types
- Power Cables: High-voltage cables for power transmission.
- Optical Cables: Used for data transmission.
- Building Wires: Used in residential and commercial buildings.
- Control Cables: Used in industrial automation and control systems.
7. Related Equipment and Accessories
7.1 Supporting Equipment
- Pay-off Machines: Used to unwind the incoming cable.
- Take-up Machines: Used to wind the extruded cable.
- Cooling Systems: Essential for cooling the extruded material.
- Packaging and Shipping: Equipment for packaging and shipping the machine.
7.2 Accessories
- Sensors and Monitoring Systems: For real-time monitoring.
- Tooling and Spare Parts: Essential for maintenance and repairs.
8. Quality and Certification
8.1 Quality Control
- Material Quality: Use of high-quality materials and components.
- Quality Certifications: ISO, CE, and other quality management systems.
8.2 Certifications
- ISO 9001: Quality management system.
- CE Certification: Compliance with European standards.
- Other Certifications: Depending on the region and application.
9. Buyer’s Guide to Selecting the Right Machine
9.1 Key Considerations for Buyers
When selecting a Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine, buyers should consider several key factors to ensure the machine meets their specific needs and operational requirements.
9.2 Key Factors to Consider
- Production Capacity: The machine’s output capacity should match the production volume required. Consider the maximum and minimum production rates.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine can handle the specific materials you plan to use (e.g., PVC, PE, PP, TPE).
- Automation Level: Consider the level of automation required. Fully automated machines may be more expensive but offer higher efficiency and consistency.
- Quality Control Features: Look for features such as temperature control, monitoring systems, and quality assurance tools.
- Maintenance and Support: Consider the availability of spare parts, technical support, and maintenance services.
- Budget and ROI: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including purchase price, installation, and operational costs.
9.3 Steps in the Selection Process
- Define Requirements: Clearly define the production needs, materials, and quality standards.
- Research Suppliers: Identify potential suppliers and manufacturers of extrusion machines.
- Request Proposals: Obtain detailed proposals from multiple suppliers, including technical specifications, pricing, and support.
- Evaluate Options: Compare the proposals based on technical features, cost, and support.
- Visit Facilities: If possible, visit supplier facilities to assess their capabilities and quality control processes.
- Make a Decision: Select the machine that best meets your requirements and budget.
10. Operational Best Practices
10.1 Daily Operations and Maintenance
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the machine clean and free of debris to prevent buildup and ensure smooth operation.
- Lubrication: Apply lubricant to moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect components for wear and tear, and replace parts as needed.
- Calibration: Ensure all sensors and control systems are properly calibrated.
10.2 Quality Control and Monitoring
- Process Monitoring: Use monitoring systems to track extrusion parameters such as temperature, speed, and output.
- Quality Testing: Conduct regular quality tests on the extruded products to ensure consistency.
- Documentation: Maintain records of production data, maintenance activities, and quality control results.
11. Maintenance of Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine
| Maintenance Task |
Importance |
Frequency |
| Lubrication of Moving Parts |
Prevents wear and tear, reduces friction, and extends the life of components. |
Regular (e.g., daily or weekly) |
| Cleaning of Extruder and Die |
Removes residue and prevents clogging, ensuring consistent material flow. |
Regular (e.g., after each shift) |
| Inspection of Electrical Components |
Ensures proper functioning of motors, sensors, and control systems. |
Regular (e.g., monthly) |
| Calibration of Sensors and Controls |
Ensures accurate operation and monitoring of the extrusion process. |
Periodic (e.g., quarterly) |
| Replacement of Worn Parts |
Replaces components that show signs of wear, such as bearings, seals, and gaskets. |
As needed |
| Cooling System Maintenance |
Ensures efficient cooling of the extruded product and machine components. |
Regular (e.g., quarterly) |
| Training and Documentation |
Ensures operators are properly trained and maintenance records are maintained. |
Ongoing |
12. Common Issues and Solutions of Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine
| Issue |
Solution |
| Pores or Bubbles in the Squeezed Layer |
Adjust temperature control, pre-dry materials, and ensure proper material storage |
| Uneven Product Diameter |
Adjust extrusion speed, check die alignment, and ensure proper concentricity |
| Material Clogging or Blockage |
Clean the extruder, filter screen, and die; ensure proper material flow |
| Inconsistent Material Flow |
Optimize temperature control, adjust screw design, and ensure proper material feeding |
| Poor Surface Finish |
Adjust extrusion temperature and ensure proper cooling |
| Excessive Wear and Tear |
Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and timely replacement of worn parts |
| Inconsistent Product Quality |
Implement quality control checks, monitor extrusion parameters, and adjust settings as needed |
| Screw and Barrel Wear |
Routine check-ups, use wear-resistant materials, and optimize screw design |
| Non-Uniform Melting |
Ensure uniform heat distribution and material flow |
| Accumulation of Material |
Routine check-ups and proper material handling |
13. Training and Operator Development
13.1 Importance of Training
- Operator Competency: Proper training ensures safe and efficient operation.
- Quality Control: Trained operators can identify and prevent issues.
- Safety: Training reduces the risk of accidents and injuries.
13.2 Training Programs
- Initial Training: Cover machine operation, safety procedures, and basic maintenance.
- Advanced Training: Cover troubleshooting, calibration, and advanced features.
- Refresher Training: Regular training to keep skills up-to-date.
13.3 Certification and Certification
- Certification Programs: Obtain certifications for operators and maintenance personnel.
- Internal Certification: Develop internal certification programs for key personnel.
14. Buyer’s Guide to Supplier Selection
14.1 Key Factors in Supplier Selection
When selecting a supplier for a Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine, buyers should consider several key factors to ensure the supplier is reliable, capable, and aligned with their needs.
14.2 Key Considerations
- Reputation and Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the industry.
- Technical Expertise: Ensure the supplier has in-depth knowledge of extrusion technology and machine design.
- Quality of Products: Verify the quality and reliability of the machines they offer.
- Customer Support: Consider the level of after-sales service, technical support, and training provided.
- Certifications and Compliance: Check for relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, etc.).
- Financial Stability: Assess the supplier’s financial health and long-term viability.
14.3 Steps in Supplier Selection
- Research and Shortlist: Identify potential suppliers through industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms.
- Request Proposals: Obtain detailed proposals, including technical specifications, pricing, and support.
- Evaluate Proposals: Compare proposals based on technical features, cost, and support.
- Visit Facilities: If possible, visit supplier facilities to assess their capabilities and quality control processes.
- Make a Decision: Select the supplier that best meets your requirements and budget.
15. Buyer’s Guide to After-Sales Service and Support
15.1 Importance of After-Sales Service
After purchasing a Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine, ongoing support and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the machine operates efficiently and reliably. A strong after-sales service network can significantly reduce downtime, extend the machine’s lifespan, and improve overall productivity.
15.2 Key Components of After-Sales Service
- Technical Support: Availability of technical experts to assist with troubleshooting and problem-solving.
- Maintenance and Servicing: Regular maintenance, calibration, and replacement of parts.
- Training and Training: Training programs for operators and maintenance staff.
- Spare Parts Availability: Quick and reliable access to genuine spare parts.
15.3 Service Levels to Consider
- Level 1: Basic Support: Basic technical support and limited spare parts availability.
- Level 2: Enhanced Support: Comprehensive technical support, regular maintenance, and faster spare parts delivery.
- Level 3: Premium Support: Full-service package including on-site support, 24/7 technical assistance, and priority spare parts.
16. Buyer’s Guide to Industry Standards and Certifications
16.1 Importance of Industry Standards
In the manufacturing and industrial sector, adherence to industry standards and certifications is crucial for ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance. For buyers of Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machines, understanding these standards can help in selecting reliable and compliant equipment.
16.2 Key Industry Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: Quality Management System: Ensures that the manufacturer has a quality management system in place.
- ISO 14001: Environmental Management: Demonstrates the manufacturer’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
- ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety Management: Ensures a safe working environment for employees.
- CE Certification: Indicates compliance with European Union safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- UL Certification: Ensures the product meets safety standards in the United States.
- IEC Standards: Relevant for electrical equipment and safety.
16.3 Importance of Compliance
- Product Safety: Ensures that the machine meets safety standards and reduces the risk of accidents.
- Quality Assurance: Ensures consistent quality and reliability of the product.
- Market Access: Compliance with international standards can open up global markets.
17. Product Testing and Quality Assurance of Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine
| Aspect |
Description |
| Quality Control Parameters |
Key parameters such as temperature, pressure, and material flow must be monitored to ensure consistent product quality . |
| Testing Equipment |
Testing equipment such as those for mechanical and physical property testing of polymeric insulation and sheathing materials are used to ensure compliance with standards like GB/T2951.11-2008 . |
| In-Line Monitoring |
In-line extrusion monitoring systems help in real-time monitoring of the extrusion process to ensure quality . |
| Material Compatibility |
The ability to handle a wide range of materials (e.g., PVC, PE, PP) is essential for versatility . |
| Quality Control Measures |
Regular maintenance, calibration, and adherence to standards such as ISO and IEC standards are crucial for maintaining quality . |
| Testing and Certification |
Testing equipment such as abrasion testers and other specialized machines are used to ensure product compliance with international standards . |
| Quality Assurance Processes |
Comprehensive quality assurance processes, including FMEA (Failure Mode and Effect Analysis) and regular inspections, are used to prevent failures and ensure reliability . |
18. Product Lifecycle Management of Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine
| Stage |
Description |
Key Considerations |
| Design & Development |
Initial design and engineering of the extrusion machine, including material selection, component design, and system integration. |
Use of simulation tools, lifecycle assessment (LCA), and eco-design principles . |
| Manufacturing |
Production of the machine components and assembly. |
Quality control, material sourcing, and manufacturing process optimization . |
| Operation & Maintenance |
Operation of the machine in the field, including performance monitoring, maintenance, and troubleshooting. |
Regular maintenance, spare parts availability, and operator training . |
| End-of-Life (EoL) |
Disposal, recycling, and recovery of the machine. |
Environmental impact assessment, recycling processes, and compliance with regulations (e.g., WEEE directive) . |
| Lifecycle Assessment (LCA) |
Evaluation of the environmental impact of the product throughout its lifecycle. |
Use of tools like LCA models, environmental product declarations (EPD), and carbon footprint analysis . |
| Sustainability & Eco-Design |
Integration of sustainability principles into product design and operations. |
Use of recycled materials, energy efficiency, and reduction of waste . |
19. Environmental and Safety Considerations
19.1 Environmental Impact
- Energy Efficiency: Choose machines with energy-efficient designs to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Waste Management: Implement proper waste management practices for materials and byproducts.
- Sustainable Materials: Consider using eco-friendly materials and processes where possible.
19.2 Safety Protocols
- Operator Safety: Ensure operators are trained on safe operating procedures and use of protective equipment.
- Machine Safety: Install safety features such as emergency stops, guards, and interlocks.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with relevant safety standards and regulations.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
20.1 What is the typical lifespan of a Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine?
- The lifespan depends on usage, maintenance, and operating conditions. With proper maintenance, a machine can last 10-15 years.
20.2 What is the average cost of a Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine?
- The cost varies widely depending on the size, features, and brand. Entry-level machines can cost 50,000to100,000, while high-end models can range from 200,000to500,000.
20.3 What are the main maintenance requirements for these machines?
- Regular maintenance includes cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of components. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule.
20.4 What are the most common materials used in extrusion?
- Common materials include PVC, PE, PP, TPE, and others. The choice depends on the application and desired properties.
20.5 How does automation affect the operation of these machines?
- Automation improves efficiency, reduces labor costs, and enhances quality control. Modern machines often include PLC control and digital monitoring.
21. Future Trends and Innovations of Wire and Cable Sheath Extrusion Machine
| Trend/Innovation |
Description |
| Advanced Materials |
Use of new materials such as nanomaterials and biomaterials to enhance performance and durability . |
| Automation and AI Integration |
Increased automation, including AI-driven control systems for precise operation and monitoring . |
| Improved Efficiency |
Development of more efficient extrusion processes with higher production speeds and reduced energy consumption . |
| Digitalization and IoT |
Integration of IoT for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote control of extrusion processes . |
| Sustainable Materials |
Use of recyclable and eco-friendly materials to reduce environmental impact . |
| Advanced Control Systems |
Advanced control systems (e.g., PLC, Siemens) for precise operation and monitoring . |
| Enhanced Quality Control |
Improved quality control through in-line monitoring and real-time analytics . |
| Customization and Flexibility |
Increased flexibility in production to meet diverse customer requirements . |


 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products