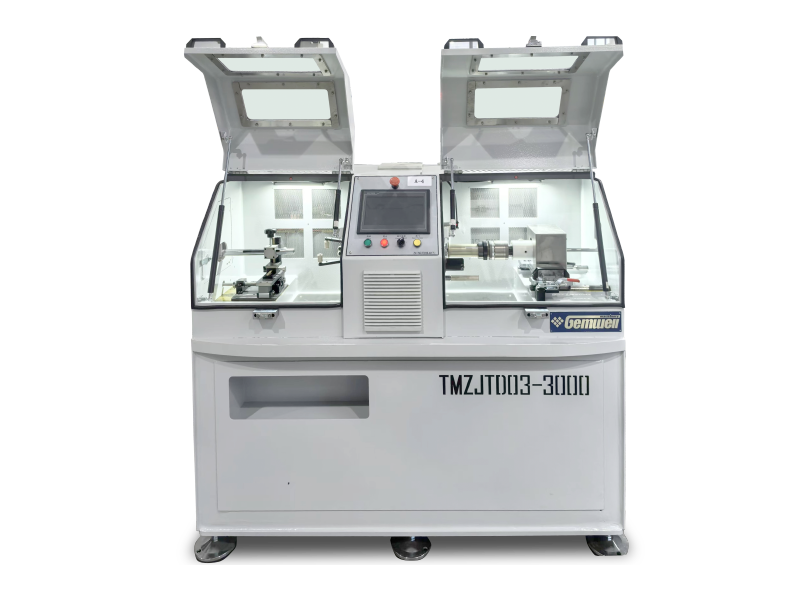
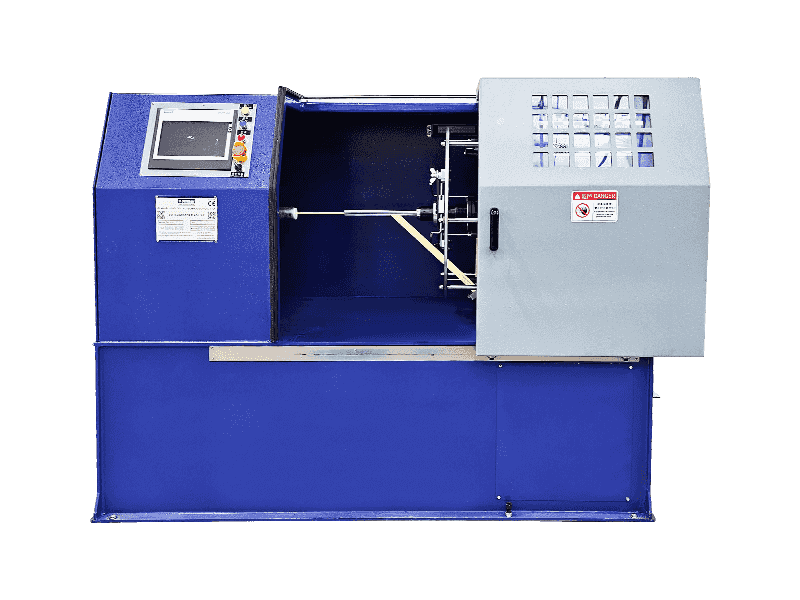
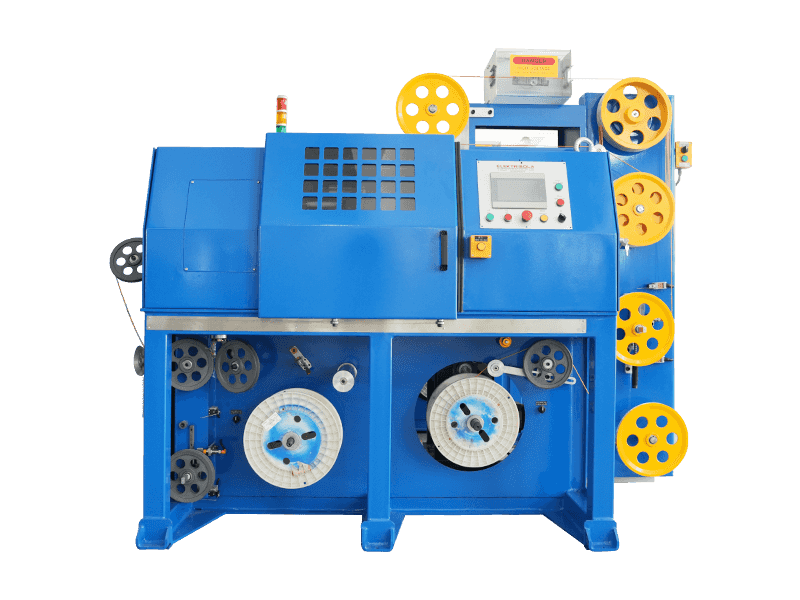
A wire and cable extruder is industrial equipment used to coat conductors with protective or functional layers. Below is a breakdown of its core aspects:
--Core Function
Material Application — Melts plastic, rubber, or polymer compounds into a fluid state. — Uniformly coats wires or cable cores with insulation, sheathing, or shielding.
--Key Components
Hopper — Loads raw material (pellets/powder) into the machine.
Barrel & Screw — Heats and compresses material via rotating screw; melts it gradually.
Extrusion Die — Shapes molten material around the conductor as it passes through.
Heating/Cooling Systems — Heating bands melt material; water baths or air jets solidify the coating.
Puller — Maintains tension to ensure even coating thickness.
--Process Steps
Feeding — Bare wire or stranded core enters the extruder.
Melting — Material flows down the barrel, softened by heat and friction.
Extrusion — Melted material is forced through the die, coating the conductor.
Cooling — Freshly coated cable solidifies in cooling tanks.
Winding — Finished product rolls onto reels.
--Output Types
Insulation — Thin polymer layers preventing electrical shorts (e.g., building wires).
Jacketing — Tough outer sleeves for abrasion/moisture resistance (e.g., industrial cables).
Semi-Conductive Shields — Controls electric fields in high-voltage cables.
Multi-Layer Coating — Combines insulation + shielding + jacket in one pass.
--Critical Design Features
Screw Configuration — Impacts mixing efficiency and material stability (e.g., avoiding degradation).
Die Design — Determines coating shape/thickness; swapped for different cable specs.
Temperature Zones — Independent controls prevent overheating sensitive polymers.
--Operational Challenges
Material Handling — Sticky compounds (like rubber) require hardened screws.
Coating Defects — Air bubbles, uneven thickness, or contaminants demand precise control.
Speed Limitations — Cooling capacity caps line speed; thick jackets need slower runs.
--Industry Variations
Dual/Triple Extruders — Layer multiple materials simultaneously for complex cables.
Cross-Linked (XL) Systems — Post-extrusion curing boosts thermal resistance.
Tandem Lines — Links extruders in series for separate core/jacket applications.
--Operator Considerations
Safety Guards — Protects against burns from barrels or moving parts.
Quick-Change Tooling — Minimizes downtime during product switches.
Scrap Management — Reclaim systems reuse trimmed edges.
 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products