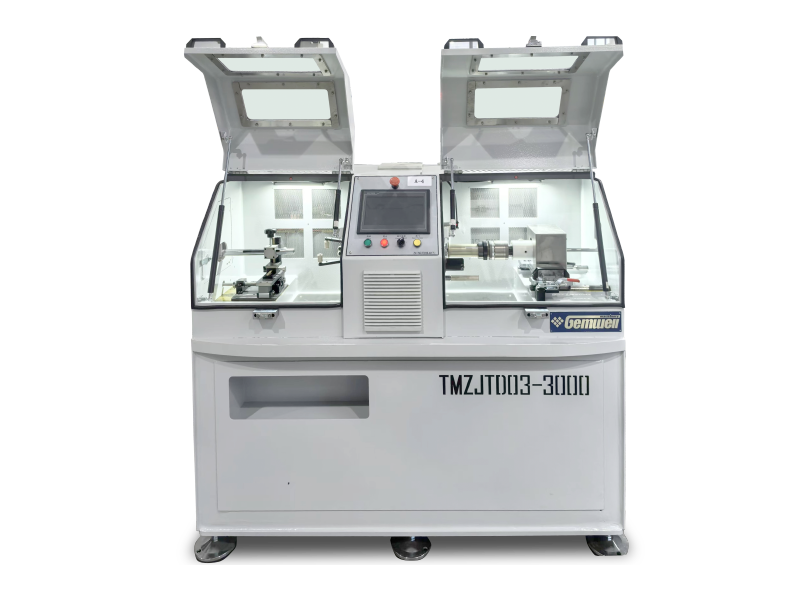
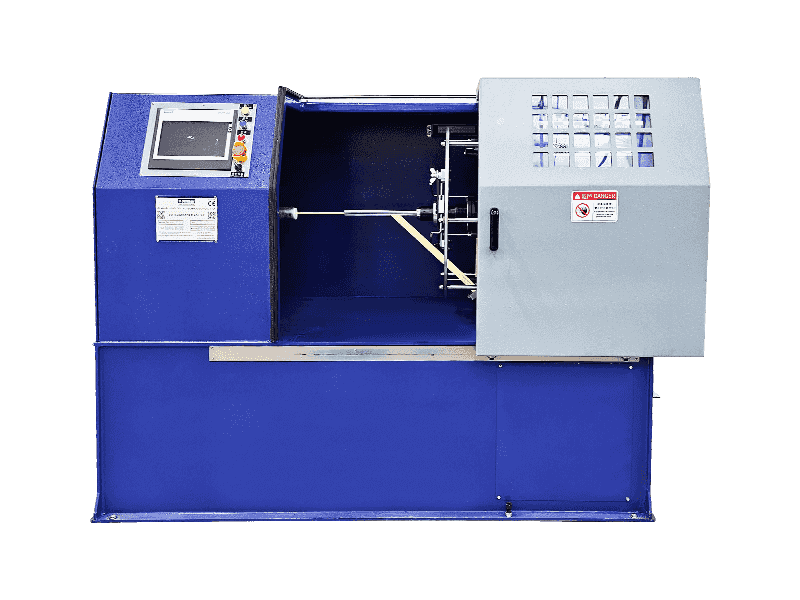
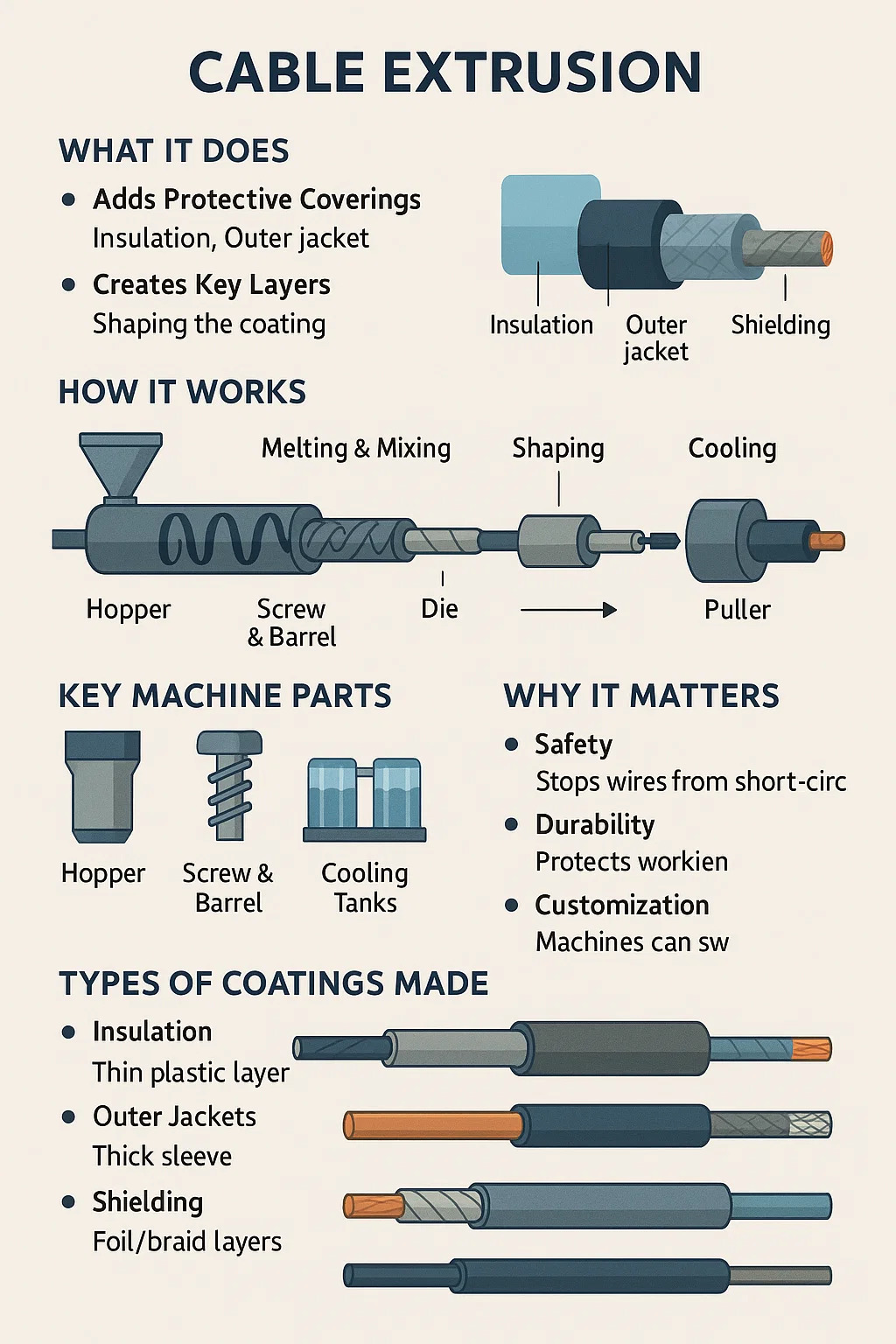
Cable extrusion is the industrial process where wires get coated with protective layers.
Content
■What It Does
•Adds Protective Coverings: Melts plastic or rubber materials to form a smooth, even coating around metal wires.
•Creates Key Layers: Applies insulation (to prevent electric shocks), outer jackets (for toughness), and special shields (like foil for blocking interference).
■How It Works
•Feeding Raw Material: Plastic pellets or powder are poured into a funnel-like hopper.
•Melting & Mixing: A rotating screw inside a heated barrel softens the material into heated barrel softens the material into a thick, molten state.
•Shaping the Coating: The melted material is forced around the wire through a custom-shaped tool (die), forming a tight layer.
•Cooling: Hot-coated wires pass through water baths or air blowers to harden the coating air blowers to harden the coating quickly.
•Winding Up: Finished cables are spinding Up**: Finished cables are spooled onto reels for storage or shipping.
■Key Machine Parts
•Hopper: Entry point for raw plastic/rubber.
•Screw & Barrel: Heats and mixes materials (like a heated meat grinder for plastic).
•Die: Metal tool that shapes the coating around the wire.
•Cooling Tanks: Sets the coating solid.
•Puller: Grips the cable gently to keep tension steady.
■Types of Coatings Made
•Insulation: Thin plastic layers (like PVC) that prevent electrical leaks.
•Outer Jackets: Tough sleeves (often rubber) resisting weather, oil, or crushing.
•Shielding: Foil/braid layers that protect signals from interference (used in internet cables).
■Why It Matters
•Safety: Stops wires from short-circuiting or shocking users.
•Durability: Protects wires from damage during installation or harsh conditions.
•Customization: Machines can switch tools to make different thicknesses, materials, or colors.
■Common Uses
•Power cords for appliances
•Wiring in buildings or cars
•Internet/phone cables
•Industrial machinery cables
 E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com
E-mail: info@gem-cablesolution.com Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
Address: No.8 Yuefeng Rd, High Tech Zone, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China | No.109 Qilin East Rd, Daning, Humen, Dongguan, Guangdong, China. English
English  English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体


 Related Products
Related Products